Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing System Engineering and Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology for Information of Shaanxi Province, School of Electronics & Information Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
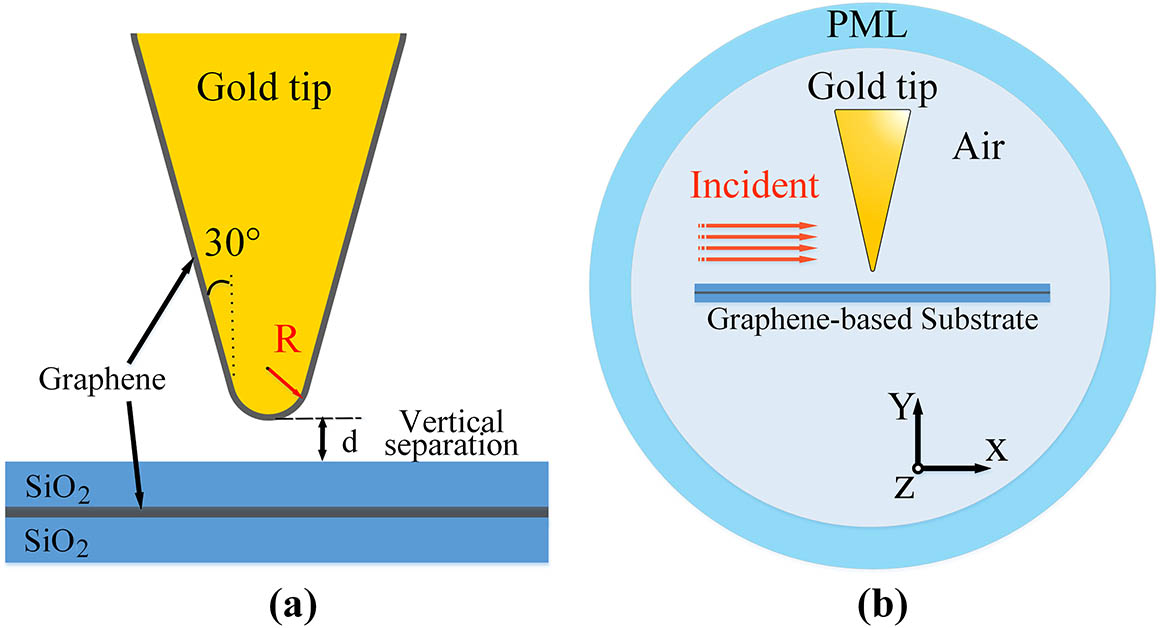
In this Letter, we propose the electronic manipulation of localized surface plasmon resonance for active tuning in near-field nanofocusing. We theoretically studied the excited graphene tuning of the nanofocusing field in few-layer graphene (FLG)-based hybrid nanotips. It is revealed that the normalized enhanced electric field can be significantly promoted to more than 300 times. It is also observed that resonant peaks can be unprecedently modified by the electron state of excited graphene that is embedded in the substrate. It shows the possibility of flexible tuning of plasmon resonances via controlling the electron excitation state of graphene for specific advanced near-field nanofocusing applications.
250.5403 Plasmonics 000.6800 Theoretical physics 260.2110 Electromagnetic optics Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 072501
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing Systems Engineering and Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology for Information of Shaanxi Province, School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
We theoretically investigate the dynamics of thermalization in Au-Ti double-layered film irradiated by a femtosecond laser pulse. A nonequilibrium thermal relaxation model is proposed to study the energy deposition and transport processes during femtosecond laser pulse heating of double-layered film. The maximum phonon temperature on the Au layer can be greatly adjusted by optimizing the thickness of the Au layer. In addition, the effect of Au-layer thickness on the thermalization dynamics of the Au-Ti system is examined in detail. This study provides a new way to increase the resistance of mirrors to thermal damage in applications of high-power lasers.
Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(Suppl): S21414
1 西安交通大学机械工程学院机械制造系统工程国家重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710049
2 西安交通大学电子与信息工程学院陕西省信息光子技术重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710049
在传统双温模型中引入傅里叶热扩散机制,提出了一种时间序列热弛豫模型。数值研究获得了飞秒激光整形脉冲与金膜作用的跨时间尺度(飞秒~纳秒)热弛豫特性及温度场时空进化规律,并获得了双温弛豫周期与整形冲间隔的依赖关系。该研究对于澄清飞秒激光与金属作用的超快热弛豫机制,调控飞秒激光微纳加工中的超快加热过程具有重要意义。
超快光学 飞秒激光 整形脉冲 热弛豫 双温模型





